CentOS下安装Munin监控服务器运行情况
By lincanbin
at 2014-12-10
0人收藏 • 5056人看过
1、切换到epel源
各版本对应命令如下:
CentOS 5.x 32bit
rpm -ivh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/5/i386/epel-release-5-4.noarch.rpm rpm --import /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-5 yum -y install yum-priorities
CentOS 5.x 64bit
rpm -ivh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/5/x86_64/epel-release-5-4.noarch.rpm rpm --import /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-5 yum -y install yum-priorities
CentOS 6.x 32bit
rpm -ivh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm rpm --import /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-6 yum -y install yum-priorities
CentOS 6.x 64bit
rpm -ivh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm rpm --import /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-6 yum -y install yum-priorities
2、安装Munin服务端、客户端
因为我只监控本机,不监控其他VPS,所以直接执行:
yum -y install munin munin-node
安装完成
3、配置虚拟主机
因为Munin生成的全是静态文件,LANMP架构下我用的是Nginx,打开nginx/conf/vhost建立虚拟主机文件,这点根据自己实际的运行环境写,我的是这样:
server {
listen 80;
server_name vps.94cb.com;
root /www/web/vps/public_html;
index index.html index.php index.htm;
error_page 400 /errpage/400.html;
location ~ \.php$ {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:88;
include naproxy.conf;
}
location / {
try_files $uri @apache;
}
location @apache {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:88;
include naproxy.conf;
}
}因为Munin要往这里写入文件,一般这个目录是www用户才有写权限的,因此要给munin写权限,为了方便我直接执行:
chmod -R 777 /www/web/vps/public_html
4、修改Munin配置
执行指令编辑Munin配置文件
vi /etc/munin/munin.conf
可以看到配置文件开头一部分是这样的。我们去掉目录配置前面的注释符,并且修改htmldir为实际的虚拟主机路径,我Nginx中指定的路径是/www/web/vps/public_html
# The next three variables specifies where the location of the RRD # databases, the HTML output, logs and the lock/pid files. They all # must be writable by the user running munin-cron. They are all # defaulted to the values you see here. # #dbdir /var/lib/munin #htmldir /var/www/html/munin #logdir /var/log/munin #rundir /var/run/munin
修改后是这样的:
# The next three variables specifies where the location of the RRD # databases, the HTML output, logs and the lock/pid files. They all # must be writable by the user running munin-cron. They are all # defaulted to the values you see here. # dbdir /var/lib/munin htmldir /www/web/vps/public_html logdir /var/log/munin rundir /var/run/munin
5、启动Munin并设置开机自启
执行以下语句启动:
/etc/init.d/munin-node start
执行以下语句添加服务并开机自启:
chkconfig --add munin-node chkconfig munin-node on
5分钟后打开你在Web服务器中设置的虚拟主机(例如http://vps.94cb.com),可以看到效果。
想马上看到的话可以直接执行(munin-cron是munin的定时任务,5分钟调用一次,手动调用的话可以直接生成统计结果的静态网站,只能以munin用户启动),不急的就别管了。
su - munin --shell=/usr/bin/munin-cron
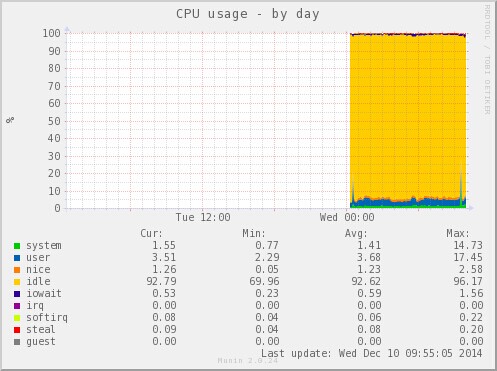
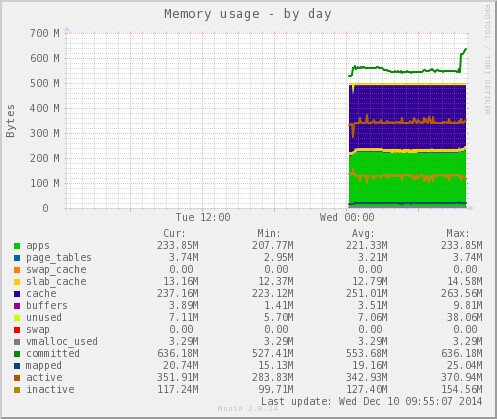
下面是Munin运行之后生成的统计图。
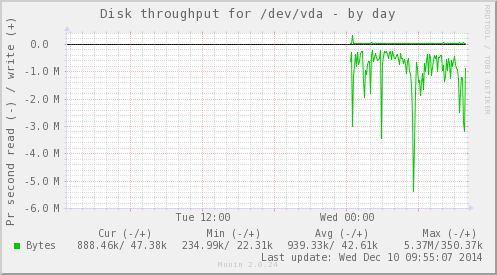
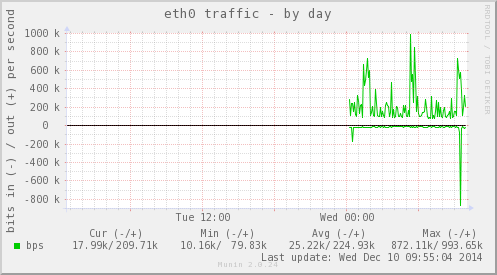
Munin还有很多插件,安装教程可以看这里:
http://gallery.munin-monitoring.org/
我也会在下面继续演示一些我需要用到的插件的安装。
- 登录后方可回帖
添加MySQL监控
Munin继续添加MySQL监控,首先执行一个软连接:
ln -s /usr/share/munin/plugins/mysql_* /etc/munin/plugins
进入mysql,添加一个用户:这里我新建的用户用户名为munin
mysql -uroot -p mysql> GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO 'munin'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '你设置的密码';
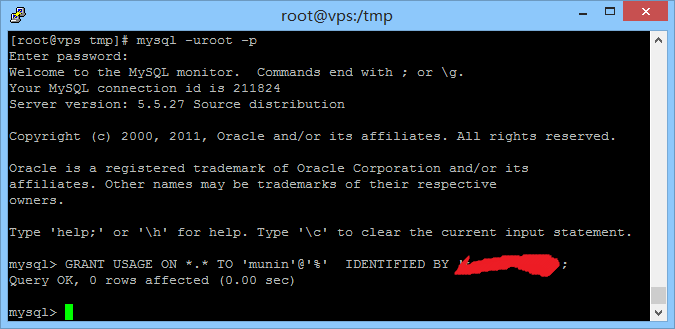
修改Munin配置文件:
vi /etc/munin/plugin-conf.d/munin-node.conf
插入以下语句并保存,然后退出:
[mysql*] user root group wheel #下面这一行如果mysql设置了环境变量可以直接访问就可以不用设置 env.mysqladmin /www/wdlinux/mysql-5.5.27/bin/mysqladmin #替换/www/wdlinux/mysql-5.5.27为你MySQL实际所在的路径 env.mysqlopts -umunin -p你设置的密码
执行以下语句:
/usr/sbin/munin-run mysql_queries
如果可以看到类似这样的结果,说明成功:
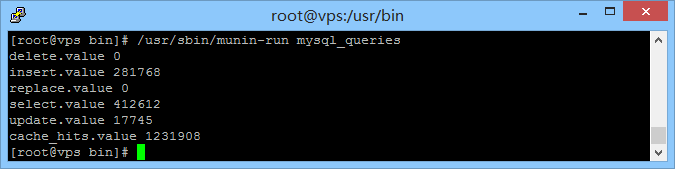
[root@vps plugin-conf.d]# /usr/sbin/munin-run mysql_queries delete.value 0 insert.value 281190 replace.value 0 select.value 411828 update.value 17737
重启Munin
service munin-node restart
几分钟后,在浏览器访问你设置的虚拟主机的域名,例http://vps.94cb.com/mysql-day.html 可以看到
点击进去,可以看到每秒执行的SQL语句次数以及类别、3306端口的I/O数据、线程数(MySQL是单进程多线程)等等数据的图表。
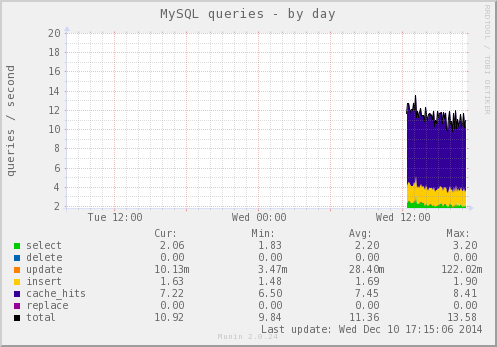
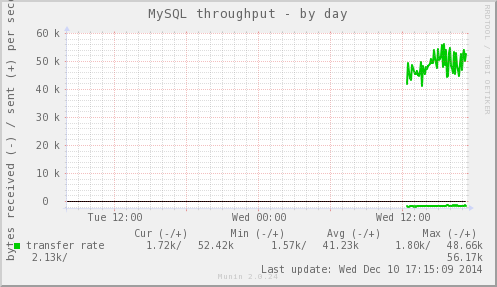
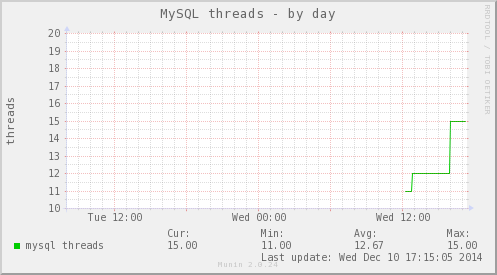
添加Nginx监控
首先要确定Nginx已经编译了nginx_status这个模块,如果没有的话,要在编译时加入这个参数
--with-http_stub_status_module
如果有的话,进行下一步:
先建立一个软连接:
ln -s /usr/share/munin/plugins/nginx_request /etc/munin/plugins ln -s /usr/share/munin/plugins/nginx_status /etc/munin/plugins
打开/新建一个VirtualHost,这里举例的配置文件是:Nginx目录/conf/vhost/vps.94cb.com.conf,添加:
location /nginx_status {
stub_status on;
access_log off;
allow 127.0.0.1;
deny all;
}我的是LANMP架构,所以最后整个vps.94cb.com.conf文件是这样的:
server {
listen 80;
server_name vps.94cb.com;
root /www/web/default;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
location /nginx_status {
stub_status on;
access_log off;
allow 127.0.0.1;
deny all;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:88;
include naproxy.conf;
}
location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf)$ {
expires 30d;
}
location ~ .*\.(js|css)?$ {
expires 12h;
}
}这个脚本打开了Nginx的统计信息,并且使得统计信息只能从本机内部访问。
然后编辑Nginx配置文件:
vi /etc/munin/plugin-conf.d/munin-node.conf
在配置文件中添加如下设置:
[nginx*] env.url http://vps.94cb.com/nginx_status
同样执行一下测试语句:
/usr/sbin/munin-run nginx_status /usr/sbin/munin-run nginx_request
如果看到类似结果,说明成功:
[root@vps tmp]# /usr/sbin/munin-run nginx_status total.value 7 reading.value 0 writing.value 3 waiting.value 4 [root@vps tmp]# /usr/sbin/munin-run nginx_request request.value 1477
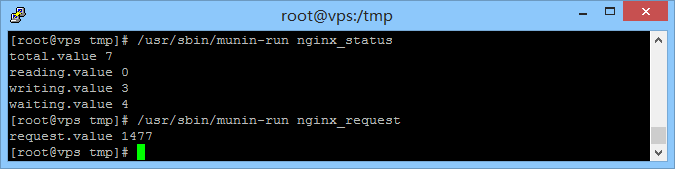
保存退出,重启Nginx和Munin
service nginxd restart service munin-node restart
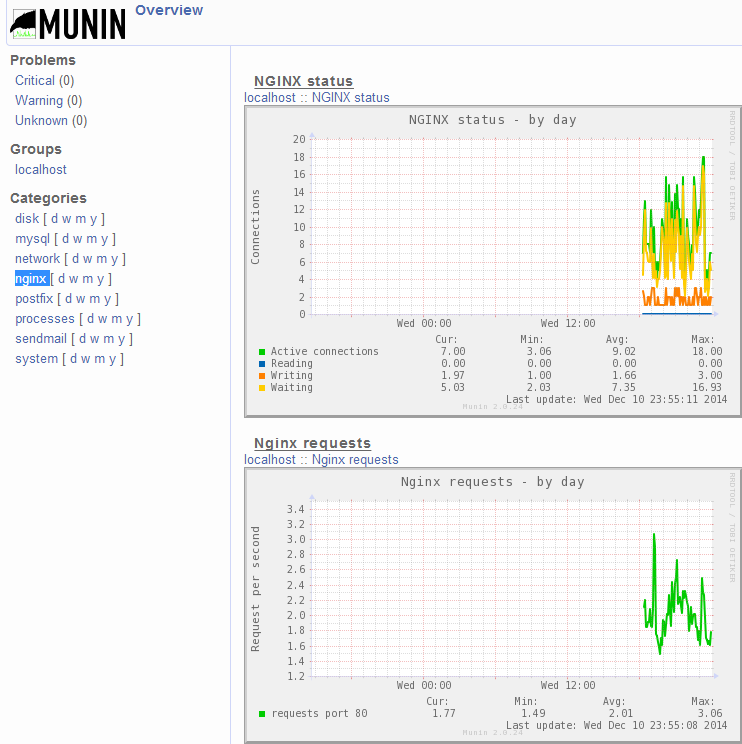
等待一段时间后,打开http://vps.94cb.com 可以观察到Nginx的统计情况,包括连接数、每秒平均请求数
需要调整绘图尺寸的可以看这里
需要调整绘图尺寸的可以看这里
http://munin-monitoring.org/wiki/faq#Q:Isthereanywaytoincreasethedefaultsizeofthemuningraphs
执行指令编辑Munin配置文件:
vi /etc/munin/munin.conf
在对应区块插入以下设置:
graph_width 1200 graph_height 400
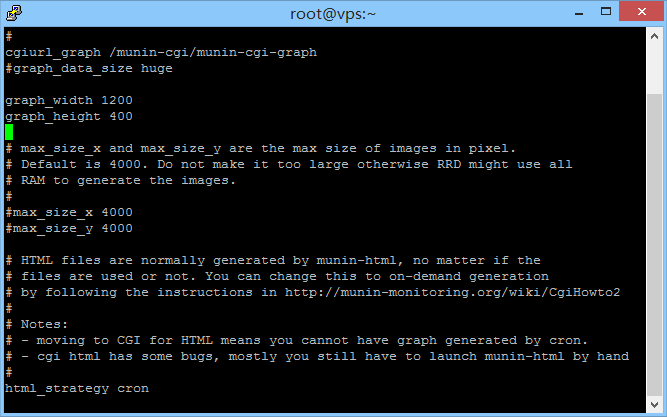
如上图,保存并退出,则可将绘图区域分辨率修改为1200*400,等待数分钟Munin绘图刷新后即可看到效果。
也可以用1楼的办法手动更新,运行:
su - munin --shell=/usr/bin/munin-cron
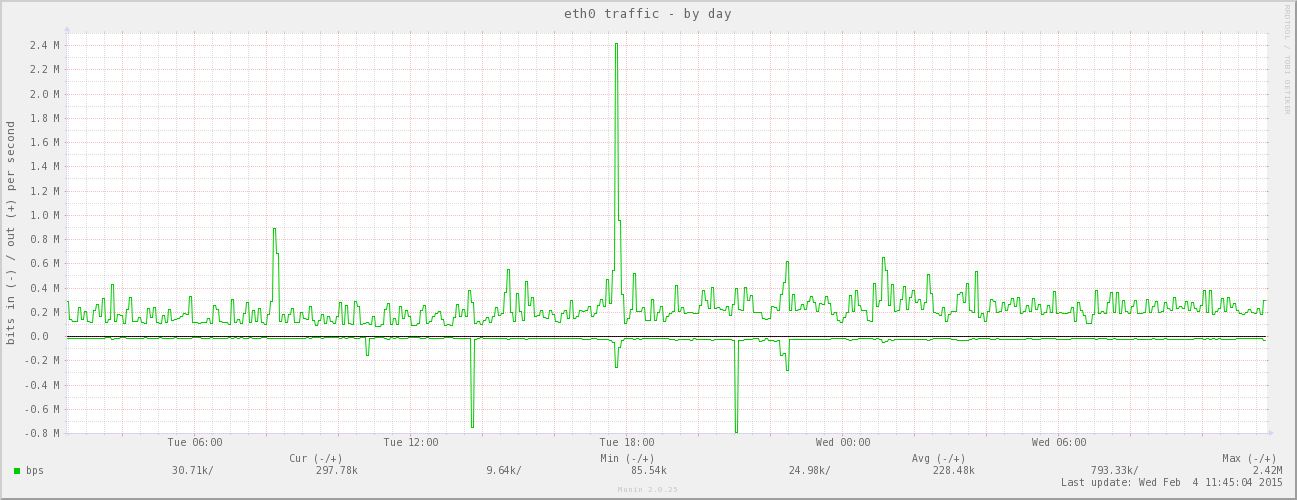
效果如图:
回复 #0 @stonemoe :
并不,一天爬虫才抓十几二十万,怎么重得起来。
回复 #0 @ivanilla :
当然不是